Impiego dell'acciaio autopatinabile in ingegneria civile e architettura
L’acciaio CorTen, introdotto dagli anni ’30, è apprezzato per la sua resistenza alla corrosione e trova impiego in strutture, facciate e installazioni artistiche, soprattutto in ambienti aggressivi. Il testo analizza il suo utilizzo in architettura e ingegneria, evidenziando lo sviluppo scientifico e le prospettive future.
L'acciaio CorTen, noto anche come acciaio resistente alla corrosione, è stato introdotto nell'ingegneria civile a partire dagli anni '30. Grazie alla sua elevata resistenza alla corrosione rispetto ai tradizionali acciai da carpenteria, l´acciaio autopatinabile ha assunto un ruolo fondamentale per applicazioni strutturali (edifici, ponti, stazioni ferroviarie, ecc.), elementi non strutturali (facciate, elementi decorativi), nonché per installazioni in siti archeologici (ammodernamento, sculture), soprattutto se esposti ad ambienti aggressivi. Questo lavoro riporta alcune considerazioni sull'utilizzo dell'acciaio autopatinabile in applicazioni di architettura e ingegneria e focalizza l'attenzione sullo sviluppo delle conoscenze scientifiche sull'argomento e sulle future tendenze connesse all’uso attuale.
Weathering steel, also known as Corrosion and Tension steel (CorTen), has a fascinating history dates back to the 1930s. Its evolution has left an indelible mark on various industries, from rail- ways to architecture. Thanks to its high corrosion resistance with respect to conventional steel, weathering steel assumed a key role for structural applications (buildings, bridges, railway stations, etc.), non-structural elements (facades, decorative elements), as well as for installations in the archaeological sites (retrofitting, sculptures), especially when exposed to aggressive environ- ments.
This paper is aimed at providing some remarks on the application of weathering steel in architec- ture and engineering applications, focusing the attention on the development of scientific and technical knowledge on the subject and the future directions raising from current utilization.
What is weathering steel?
Weathering steel, also known as low-alloy steels or Corten by the trade name, is a high strength low alloy steel. It was developed by the Vereinigte Stahlwerke AG in Germany in 1928 and by the American company United States Steel Corporation in 1933 when it was facing a unique chal- lenge: the need for rugged, corrosion-resistant steel for railway coal wagons. This was an era when America’s railways and collieries demanded materials that could endure the harshest condi- tions, thus Corten was born as a response to this demand.
Since the first application, it was evident the success of this steel because it was lighter and more resistant to impact and corrosion than conventional steels. From the 1960s onwards, engineers and architects expanded the application of weathering steel in the field of civil engineering exploiting its improved resistance to cor- rosion for a wide range of construction projects.
Weathering steel is the result of a precise combination of alloying elements with addition of chromium, copper, silicon and phosphorus during the production process. Such a combination provides the resistance to corrosion to material, because of the development of a protective rust layer (known as iron oxide) that forms and stabilizes correctly over time under the right condi- tions in terms of weather conditions. This rust layer, unlike the porous oxide layer found in the conventional steels, does not hold moisture and inhibits further corrosion and the result is a distinctive color appearance and the most important resulting in long-term durability, which makes this material maintenance-free. The latter aspect incentivized the use of weathering steel and its growing in various technical sectors, industry and construction.
It has become an ideal material for engineers, architects, manufacturers, landscapers, urban planners and artists, whose chose was often limited due to its high cost with respect to other traditional materials (e.g., reinforced con- crete or masonry).
Other benefits coming from the application of weathering steel are the cost-effective choice over time. Although weathering steel is slightly more expensive than conventional steel, savings from the elimination of the paint system offsets the additional material cost.
Attractive appearance of weathering steel bridges and in general in structures and non-structures buildings often blends pleasingly with the environment and improves over the years because of the formation of a stable oxide layer which usually turns into a dark brown color. The ideal environment in which weathering steel has to be applied in order to achieve the better performances are rural and urban locations. This ideal situation is of course linked to a weathering steel exposed to alternate cycles of wetting and drying by clean rain, which would lead to the formation of a very dense, tightly adhering and stable oxide layer . In this sense, environments where high concentrations of strong chemical or industrial pollutants are present should be avoided, especially marine environments.
This paper is aimed at providing some remarks on the application of weathering steel in architec- ture and engineering applications, focusing the attention on the development of scientific and technical knowledge on the subject and the future directions raising from current utilization.
An overview of technical literature
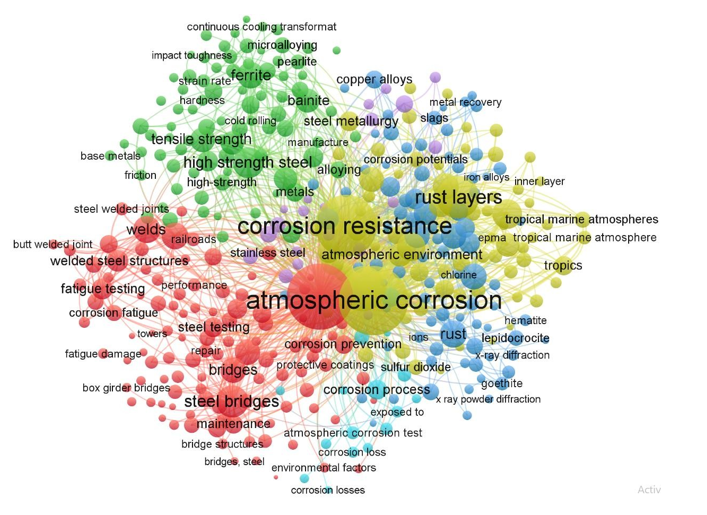
Relevant literature data available from the source Scopus were analyzed in order to identify theo- ries, methods, and gaps in existing research for constructing and visualizing a bibliometric network (Fig. 1) by using the VOSviewer application. The keyword “weathering steel” has to be written into the search document by applying article title, abstract, keywords (in the Scopus web- site). The total documents found are 1,556, which have been exported in .csv format by applying citation information and abstract and keywords. Paper from the year 1968 (the oldest) to the most recent one that corresponds to the current year 2024, can be observed. Once the file is exported, the VOSviewer was used, where a new map based on bibliographic data has to be created by choosing data source from Scopus and by selecting the type of analysis co-occurrence and all keywords. And the last step is verifying the selected keywords by removing repeated keywords such as weathering steel and steel.
...Continua a leggere nel PDF in allegato.
L'intera memoria è in lingua inglese.
La presente relazione è stata presentata in occasione del XXIX Congresso CTA, svoltosi a Milano il 26 e 27 settembre 2024.
Architettura
L'architettura moderna combina design innovativo e sostenibilità, mirando a edifici ecocompatibili e spazi funzionali. Con l'adozione di tecnologie avanzate e materiali sostenibili, gli architetti moderni creano soluzioni che affrontano l'urbanizzazione e il cambiamento climatico. L'enfasi è su edifici intelligenti e resilienza urbana, garantendo che ogni struttura contribuisca positivamente all'ambiente e alla società, riflettendo la cultura e migliorando la qualità della vita urbana.

Costruzioni
Costruzioni: su INGENIO articoli tecnici, normative e innovazioni per progettare, realizzare e gestire opere edilizie e infrastrutture.
Costruzioni Metalliche
Le costruzioni metalliche rappresentano una scelta strategica per strutture leggere, sicure, resistenti e sostenibili. Scopri su INGENIO tecniche, norme e soluzioni per progettare con l’acciaio.

Edilizia
Esplora il mondo dell'edilizia, il settore dedicato alla progettazione, costruzione, ristrutturazione e manutenzione di edifici e infrastrutture. Scopri come la normativa italiana, come il Testo Unico dell'Edilizia (D.P.R. 380/2001) e le Normative Tecniche per le Costruzioni (NTC), regolano le pratiche edilizie per garantire sicurezza e qualità. Approfondisci il significato etimologico del termine "edilizia" e come le leggi locali e regionali influenzano la costruzione e gestione degli immobili.
Condividi su: Facebook LinkedIn Twitter WhatsApp